Research and Publications
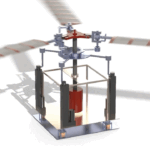
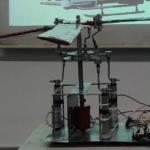
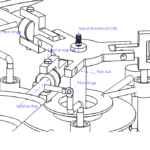
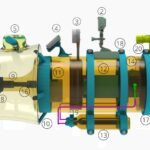
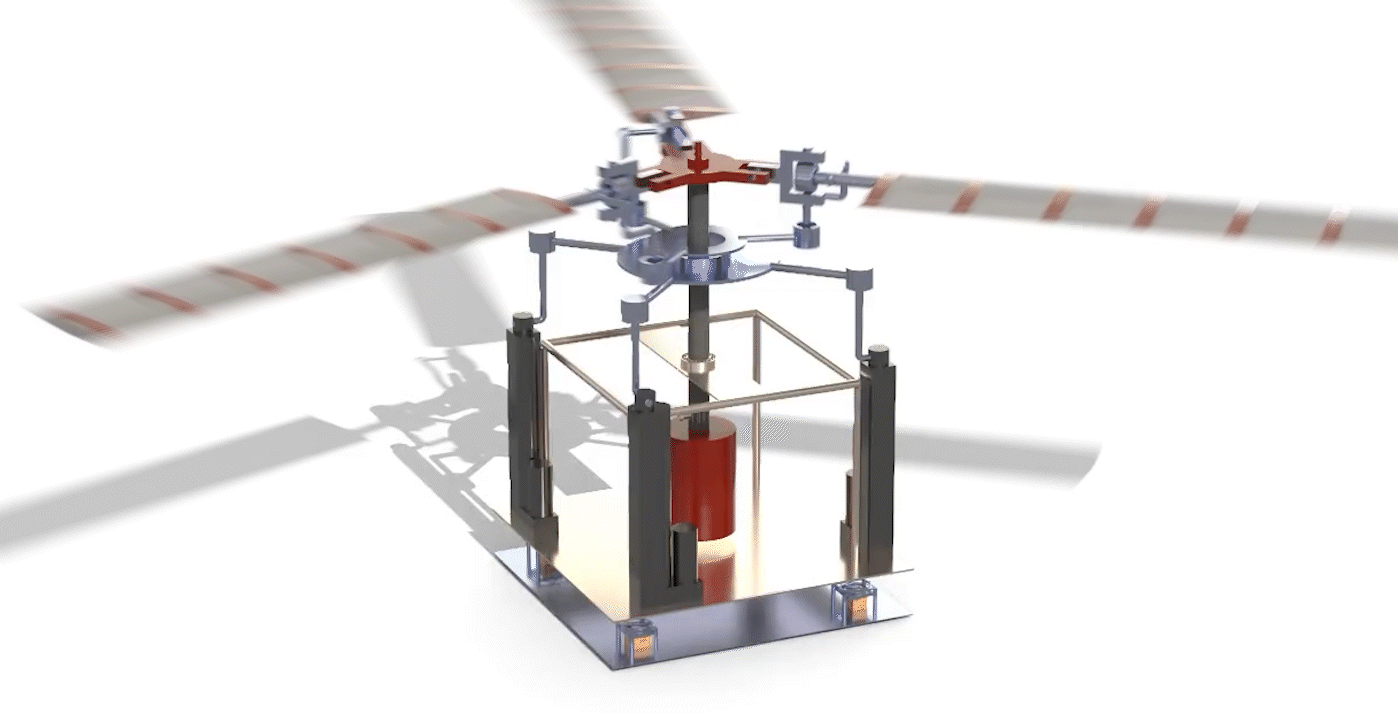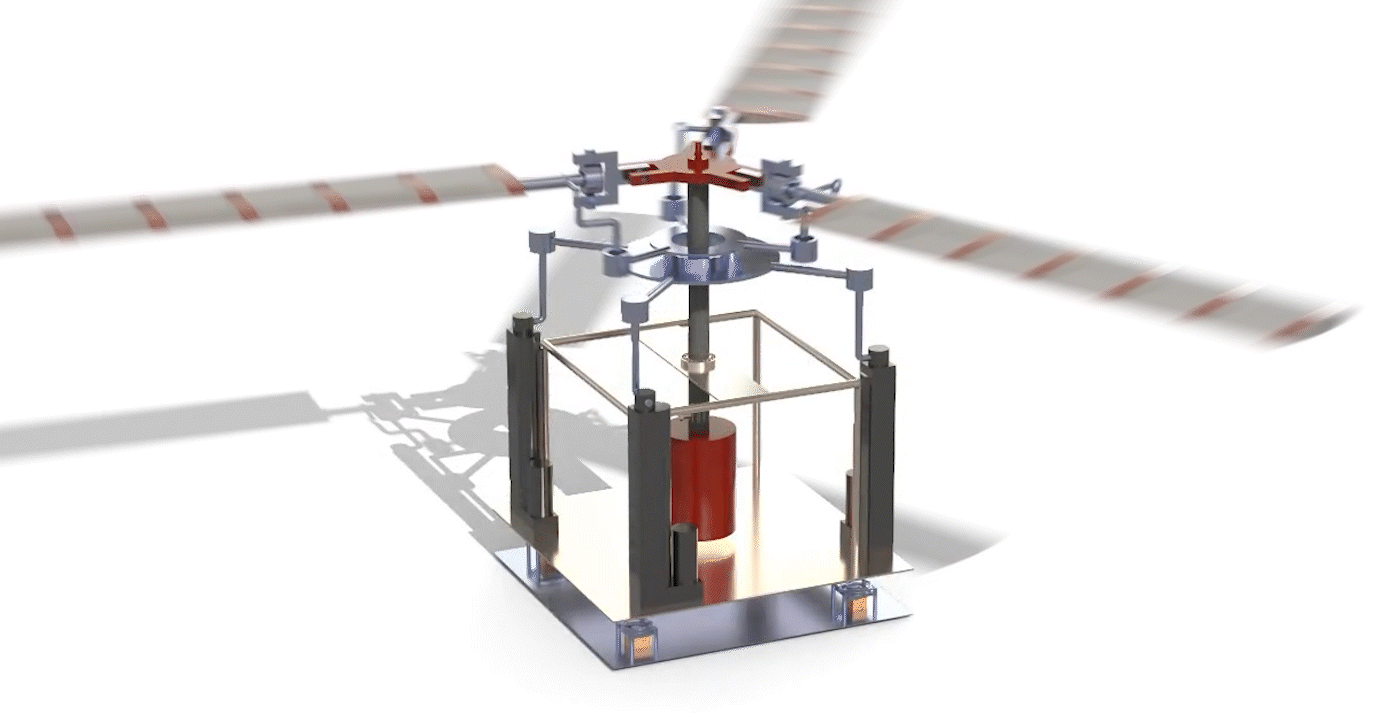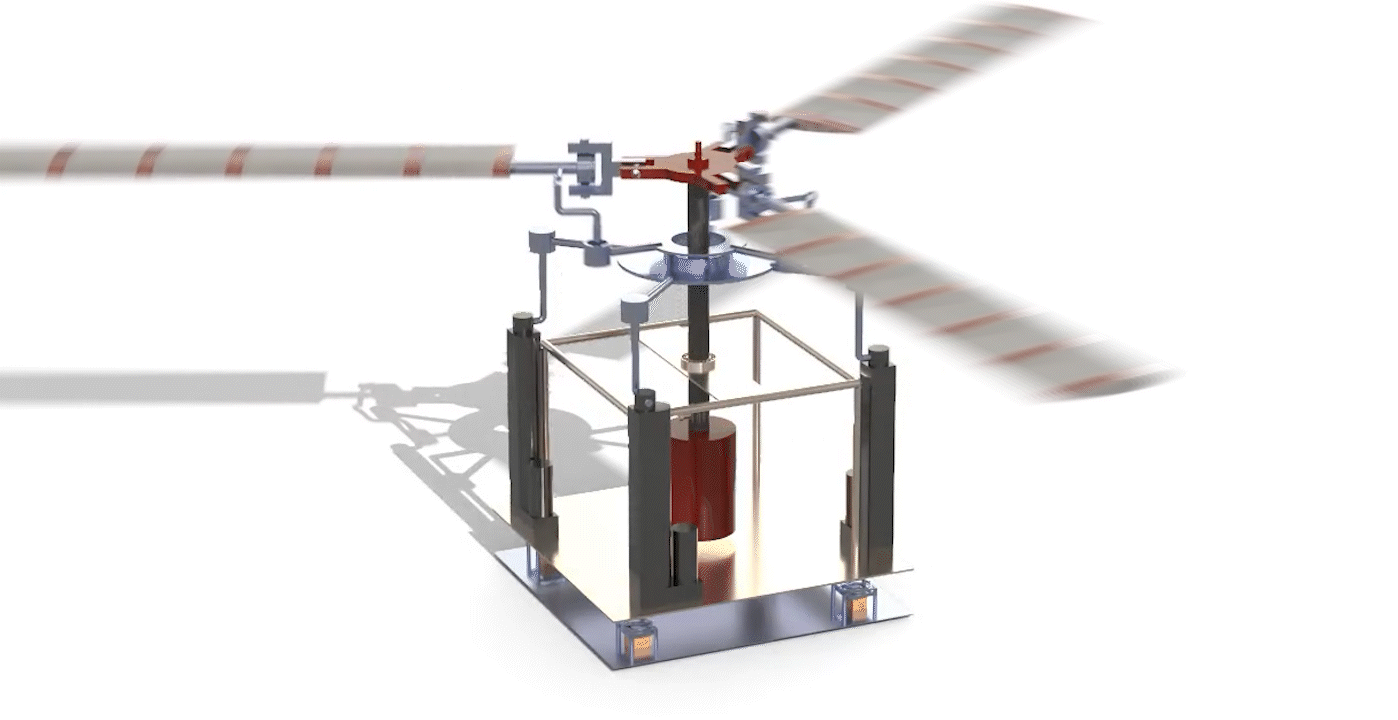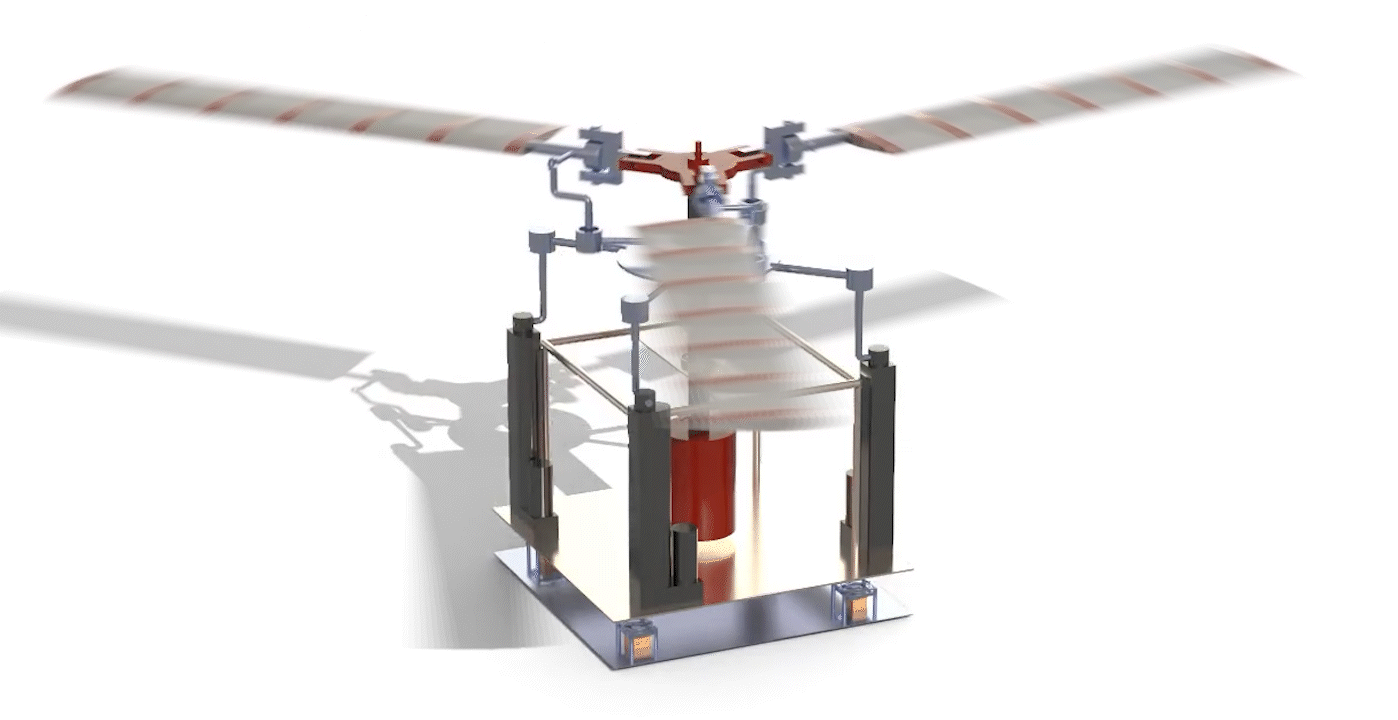
Design, Analysis, and Fabrication of A Fully Articulated Helicopter Main Rotor System (2019)
– Team Leader, Undergraduate Thesis Project, Dept. of AE, MIST
Keywords: Rotor Mechanism, CFD, Structure, Fabrication and Testing, Aerodynamics
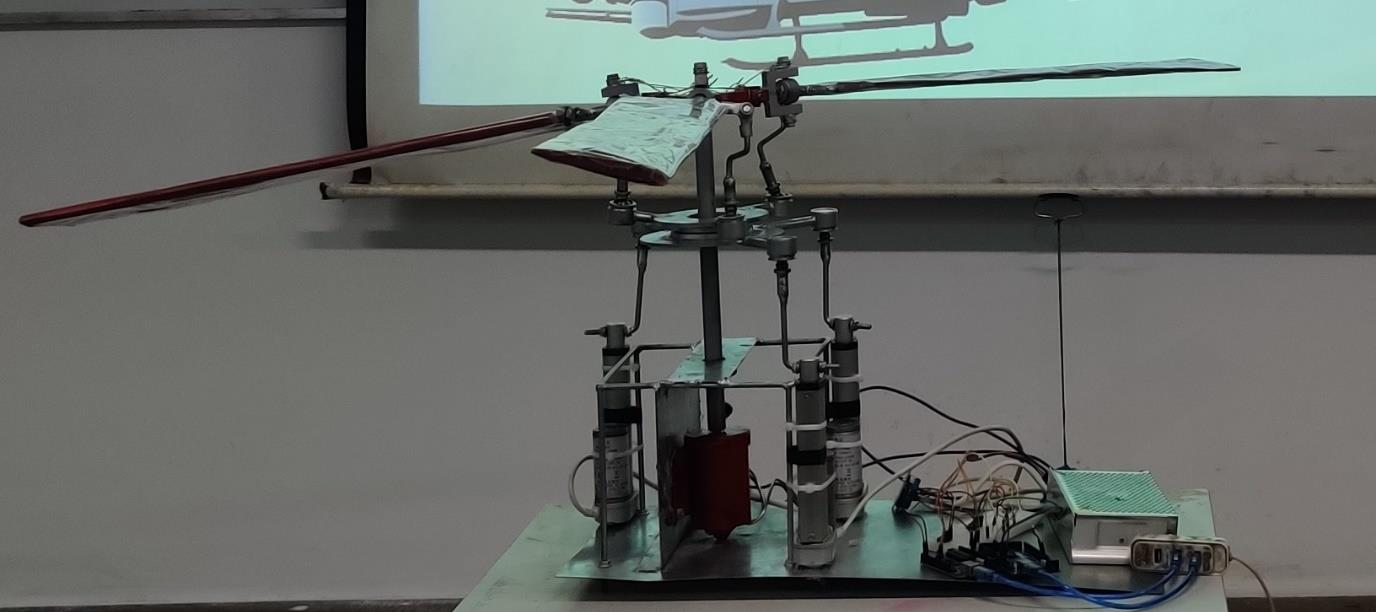
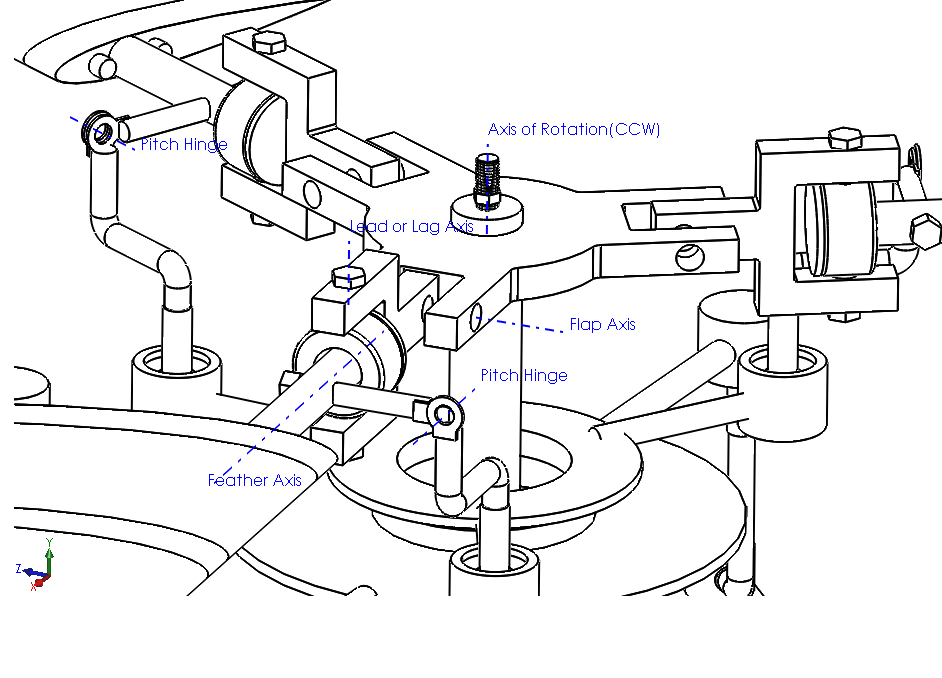
Abstract: The rotor mechanism performs thrust vectoring by changing the collective or cyclic pitch of the blades. The blades are connected to the hub through articulated joints, enabling flapping, feathering, and lead or lag motion of the blades. Three linear actuators deflect the stationary lower swash-plate, which in turn deflects the upper swash-plate, thereby changing the pitch of the blades collectively or cyclically. Several load sensors, which are placed under the base, are used to measure the thrust and the direction of thrust when the blades are rotating at certain RPMs. The input signals fed to the actuators and output signals received from load sensors are driven and monitored by an Arduino microcontroller via a software interface.



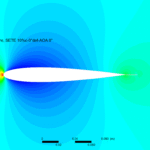
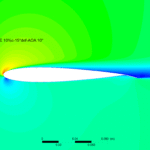
Experimental and Computational Strategies for Improving the Aerodynamic Performance with Static Extended Trailing Edge (2023)
– Physics of Fluid, AIP Publishing, ISSN 1089-7666 (In Review)
Author: Nazib Eadin, Azizur Rahman
Keywords: Flow Control, Wind Tunnel Testing, Computational Fluid Dynamics, Aerodynamics, Lift Enhancement
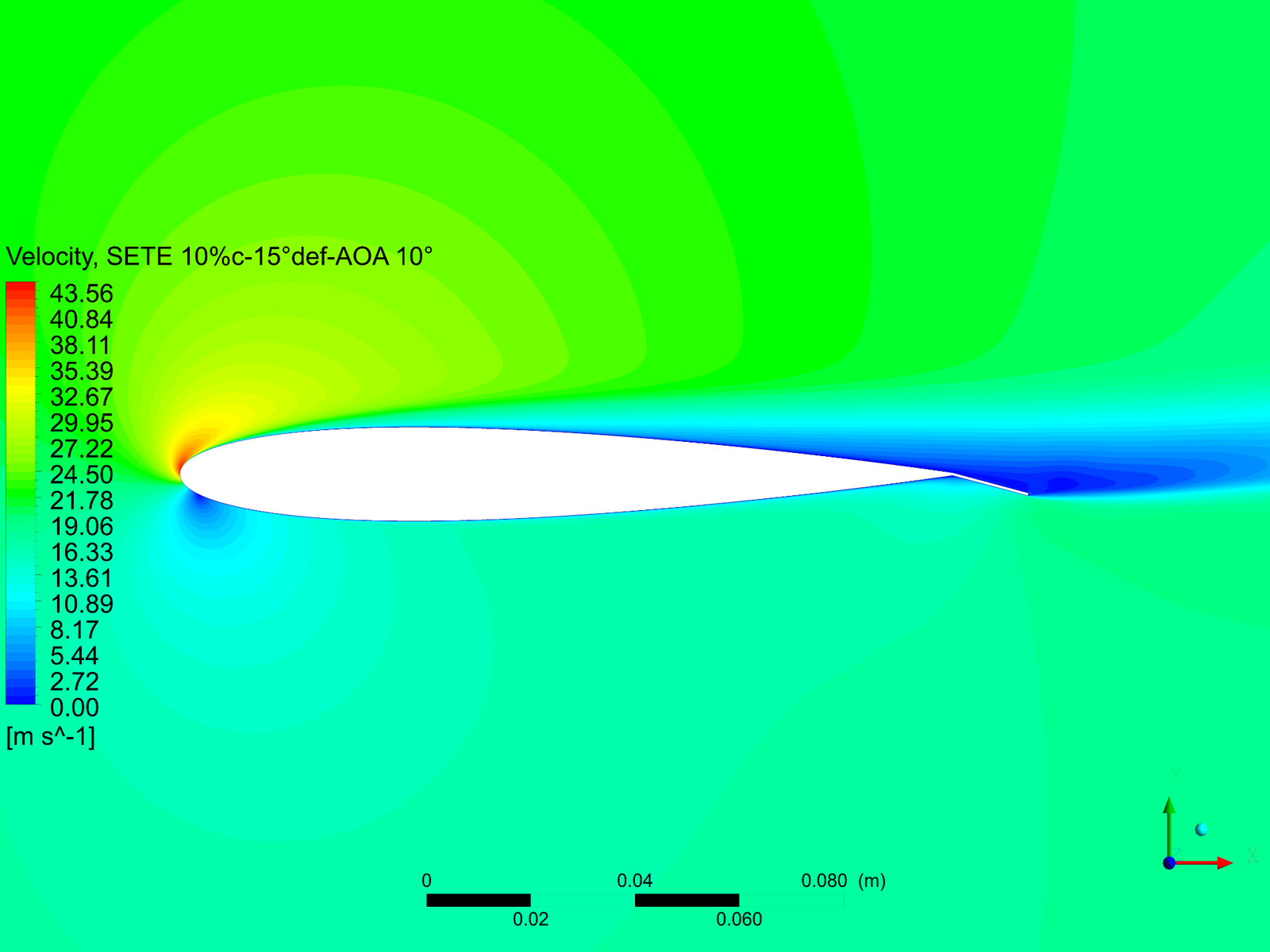
Abstract: An open-loop wind tunnel experiment and CFD simulations are carried out on several Static Extended Trailing Edge (SETE) attached to the 150𝑚𝑚 × 300𝑚𝑚 wing model to investigate the effect of a SETE on the aerodynamic characteristics at low Reynolds. A thin extended trailing edge of length 20% of the chord and 15° deflection appears to generate 74.24% more lift concerning the baseline model. SETE enables a smooth, gradual stall, resulting in more time for stall recovery. A high benefit margin makes SETE an ideal option for achieving greater cruise flight efficiency.






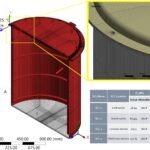
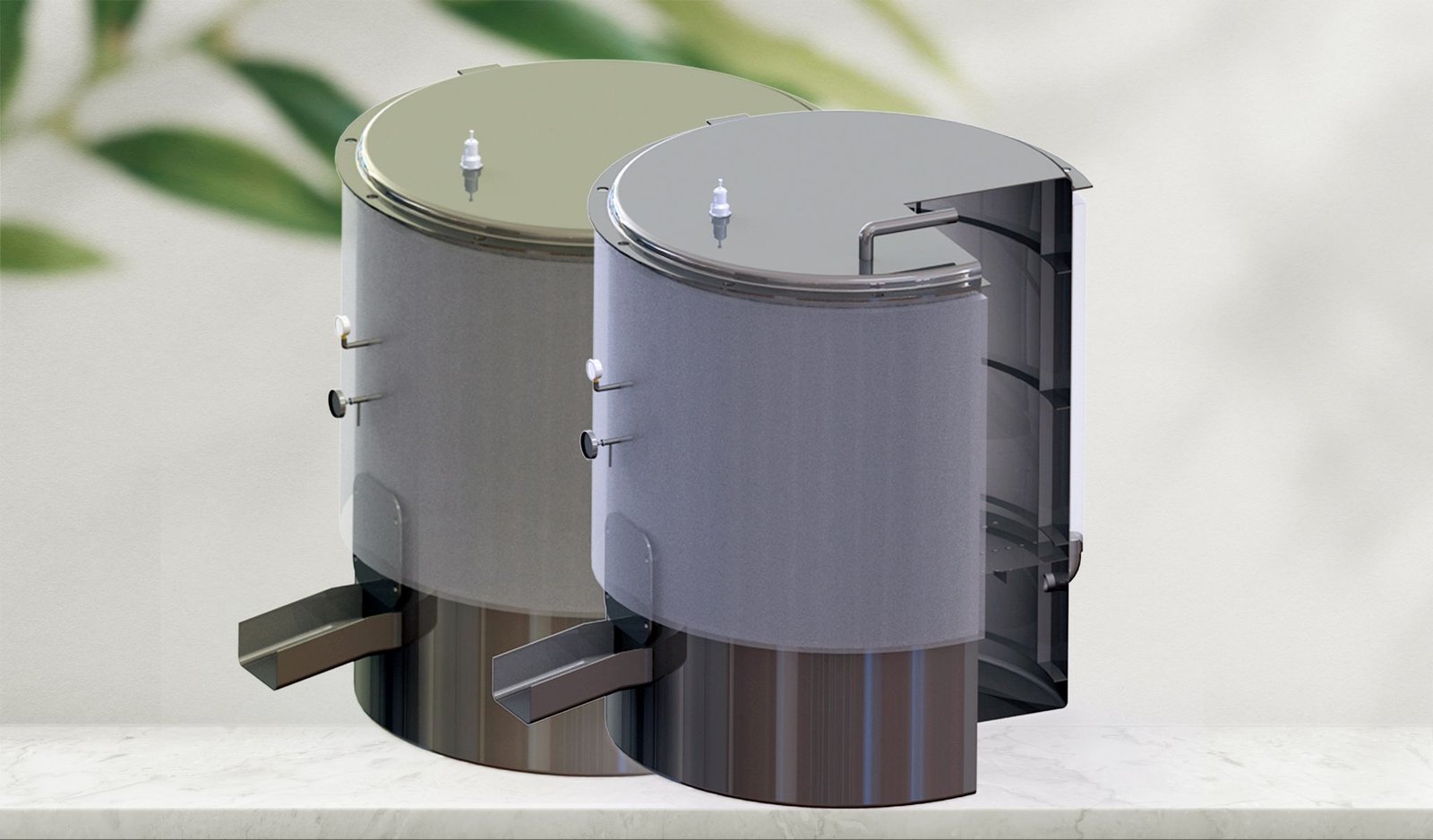
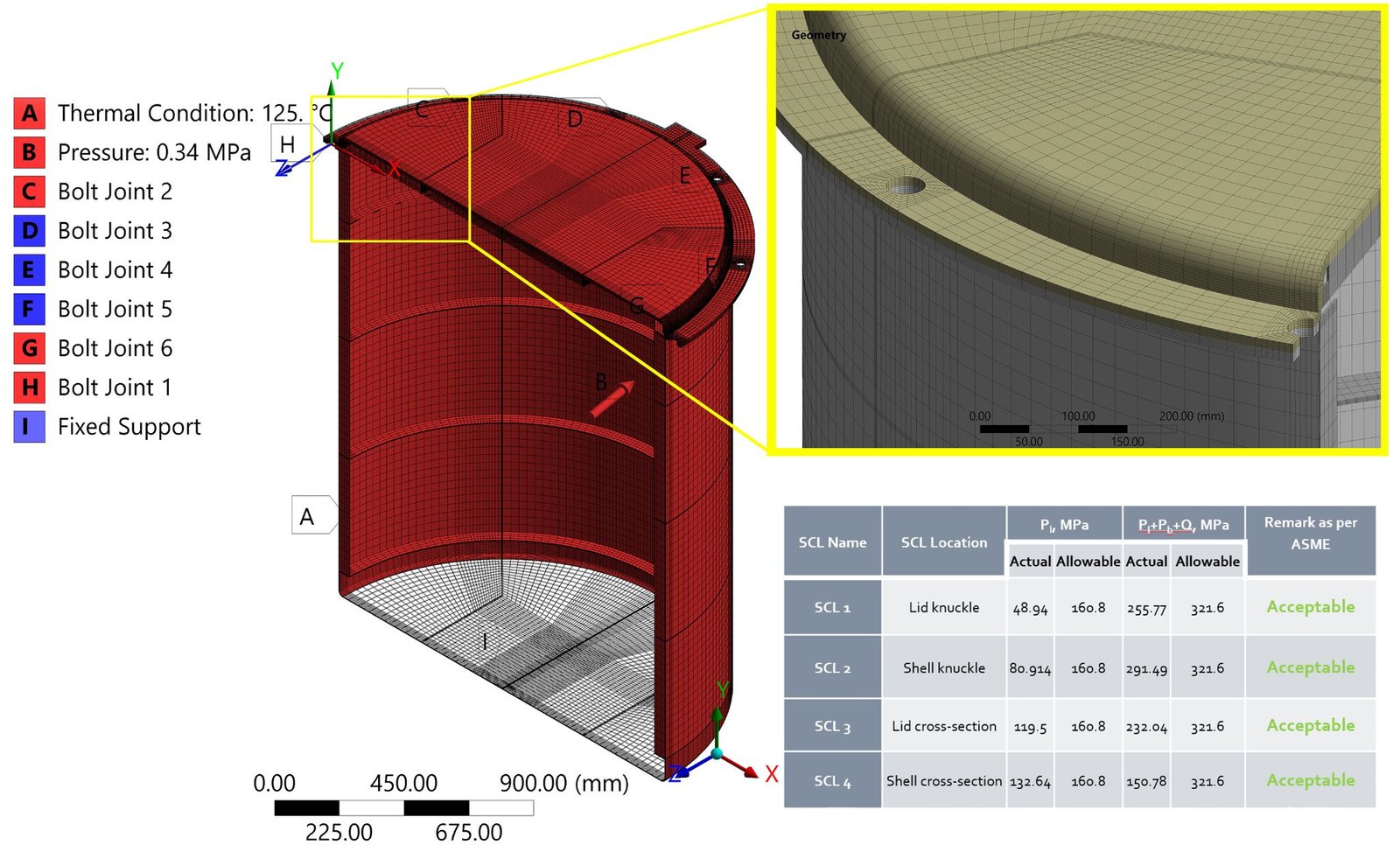
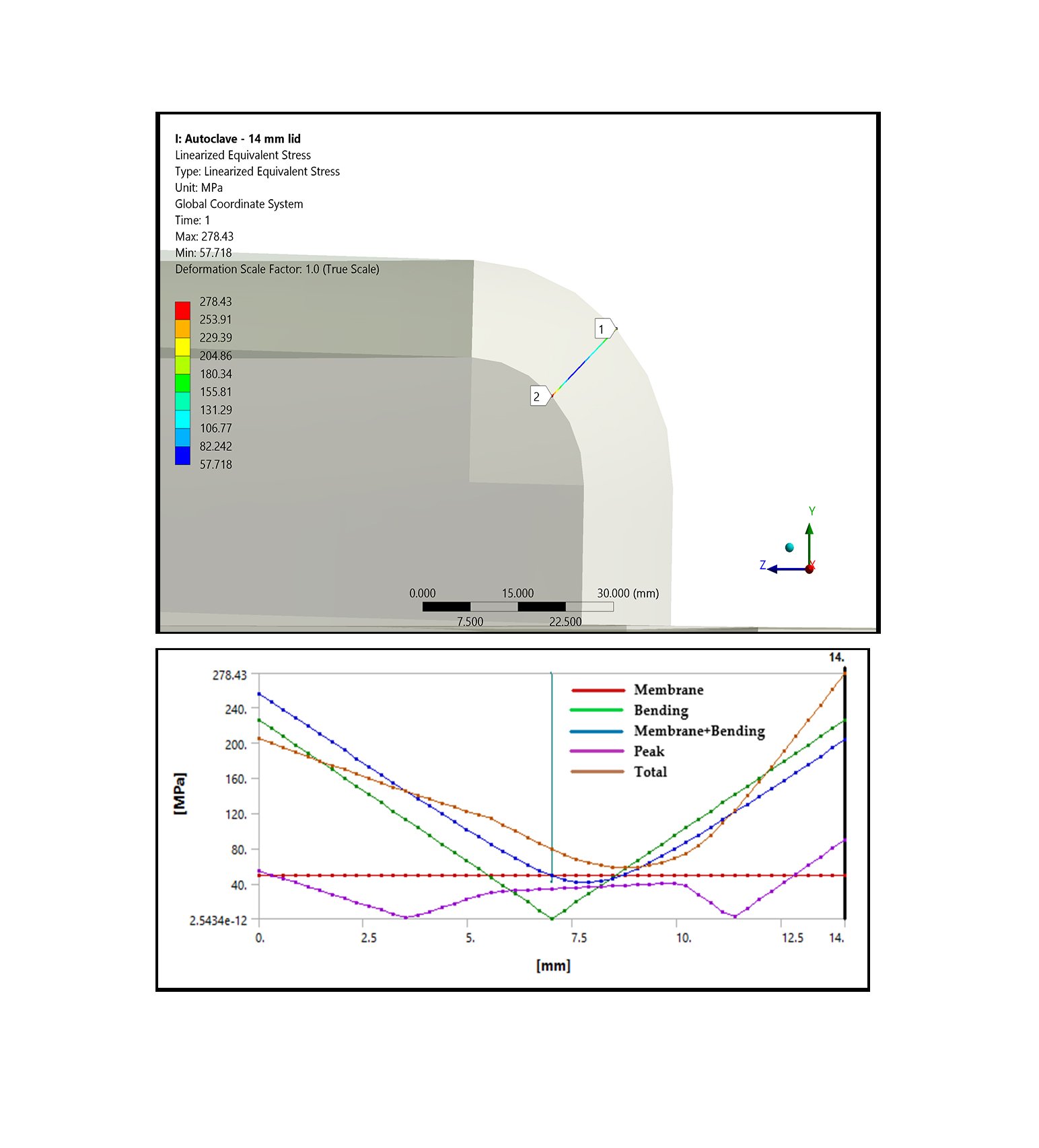
Optimizing Palm Oil Extraction: Design and Performance Analysis of a Locally Manufactured Autoclave for Palm Fruit Processing (2023)
– Sustainability-Special Issue, MDPI Journal, ISSN 2071-1050 (In Review)
Author: Chowdhury Raihan, Nazib Eadin, Raad Haque, and Suhail Ragib
Keywords: Pressure Vessel Development, Autoclave, Palm Processing, FEA, ASME validation, Finite Element Analysis, Fatigue Assessment
Abstract: This study presents the design and development of a pressure vessel/autoclave that pertains to a palm fruit sterilization unit. Palm fruit goes through several steps before the final extraction of oil from the fruit, in which boiling the palm fruit under certain conditions is one of the vital steps for the yield ratio of oil from the palm seed. This study consists of several research and development studies to design and develop an autoclave machine, considering the process safety, ASME design code for pressure vessels, and simulation data to validate the endurance of the designed autoclave under local manufacturing facilities. A computational static structural analysis and fatigue assessment is conducted to validate the design requirements according to the ASME design code and manufacturing standard. The maximum von Mises and principal stresses generated throughout the pressure vessel do not surpass the calculated material’s (SS 304) yield strength. The fatigue damage factor measured is significantly less than 1. The total number of cycle counts exceeds the total number of design cycles evaluated.

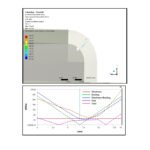
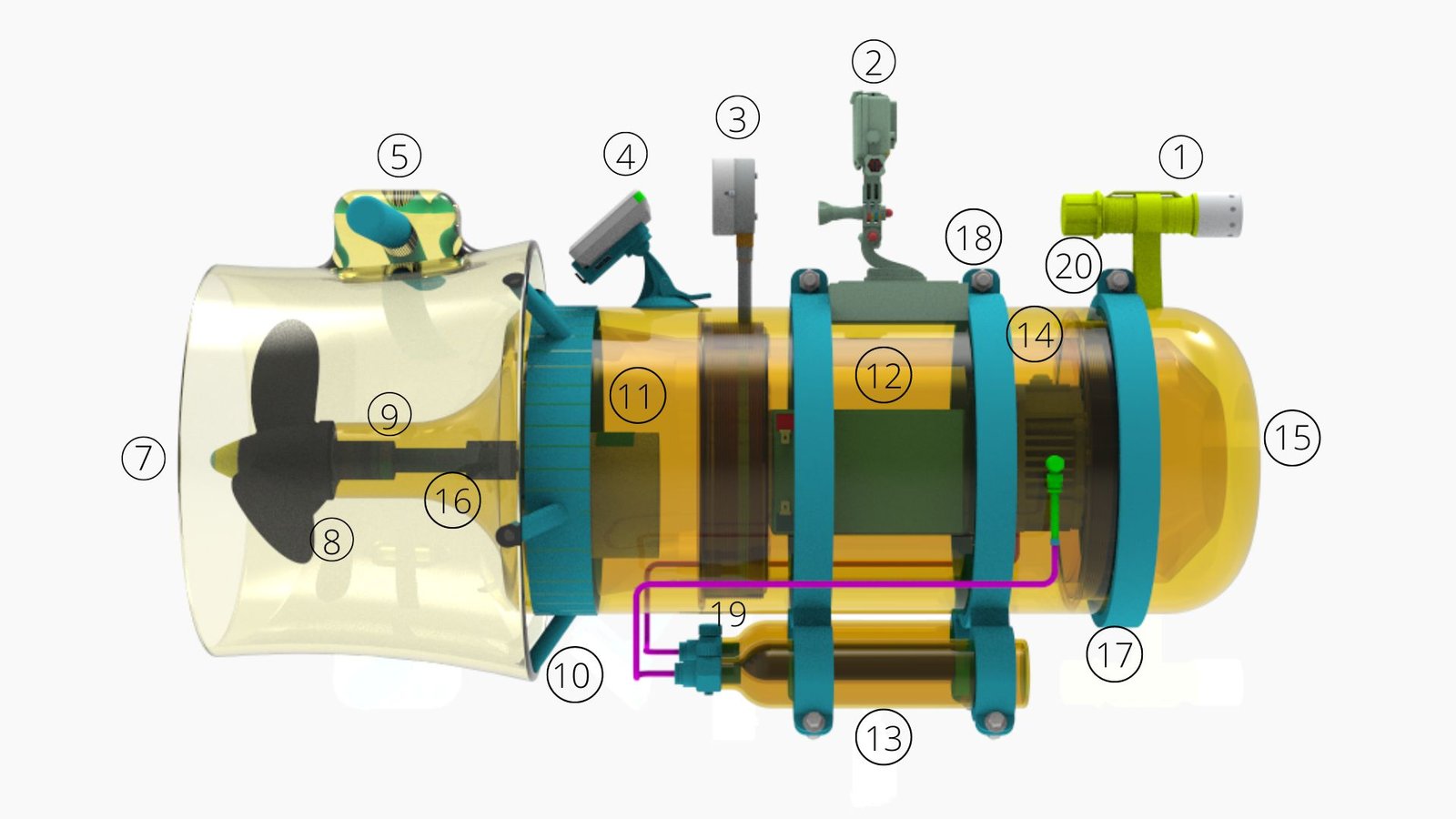
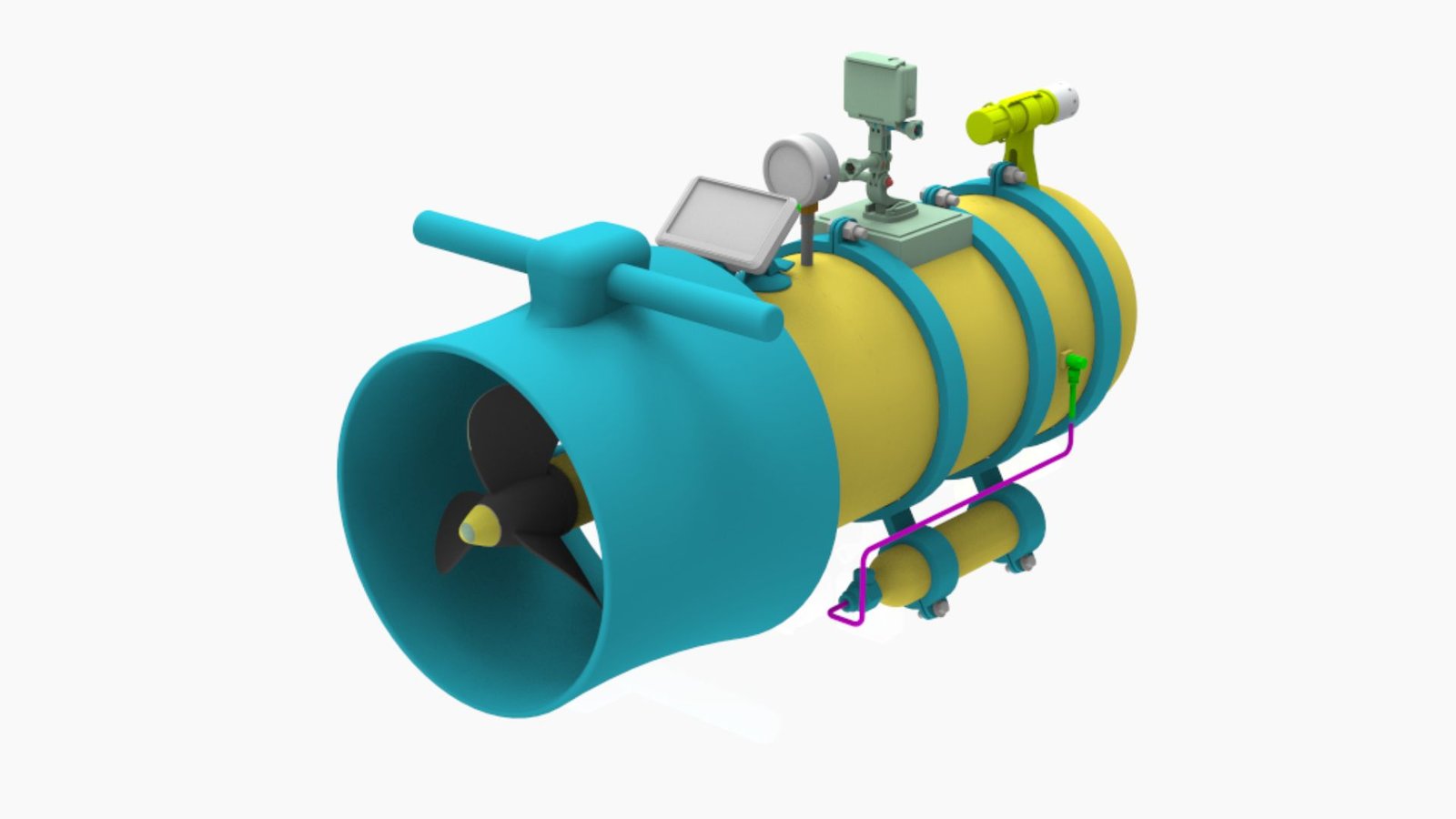
Design and Fabrication of a Diver Propulsion Vehicle Using Local Manufacturing Technology (2023)
– Sustainability-Special Issue, MDPI Journal, ISSN 2071-1050 (In Review)
Author: Chowdhury Raihan, Nazib Eadin, and Raad Haque
Keywords: Diver Propulsion Vehicle, Fabrication and Testing
Abstract: Diver Propulsion Vehicles, or DPVs, are commonly used by scuba divers, particularly in the defense industry. While there is no mandatory set of design requirements for military-grade DPVs, various configurations and designs are available. In this project, we aimed to apply theoretical knowledge of marine and mechanical engineering to design and fabricate a standard DPV. We considered key hydrostatic parameters during calculation, utilizing input data from established DPV models. ANSYS simulations demonstrate the efficiency of our design in hydrodynamics. An inventive liquid cooling device handles the generation of electro-mechanical heat. An O-ring-based sealing is incorporated in the DPV to protect the battery from becoming ineffective. The DPV tested satisfactorily, and Bangladesh Navy troops successfully operated it. While experimenting, we observed a favorable velocity profile and effective maneuvering performance, enduring a successful leak test with maximum tolerance. However, the model is currently manual in some aspects, and we propose further development to convert it into an advanced automated DPV.



A Fast Load Variation Adaptable Organic Rankine Cycle-based Waste Heat Recovery System Using Cost-Effective Thermal Oil and Working Fluid
– presented at the 2nd International Conference, ICMEAS2022
Author: Noor Hasan, Dr. A.H.M. Saadat, Dr. A.M. Shahabuddin, Nazib Eadin, and Rahman
Keywords: Organic Rankine Cycle, Waste Heat Recovery, Palm Olein, n-Pentane
Abstract: A design proposition is made of an ORC-based Waste Heat Recovery system, in which the authors proposed a robust electro-mechanical control system that allows frequent load variation without the time lag associated with SCADA, and Delta PLC S7-200.